In this post, you will learn about the OSI model, the layers of OSI model, the functions of the OSI model, and so on in detail with a basic explanation and example.
So let’s start learning all the things one by one.
What is OSI model?
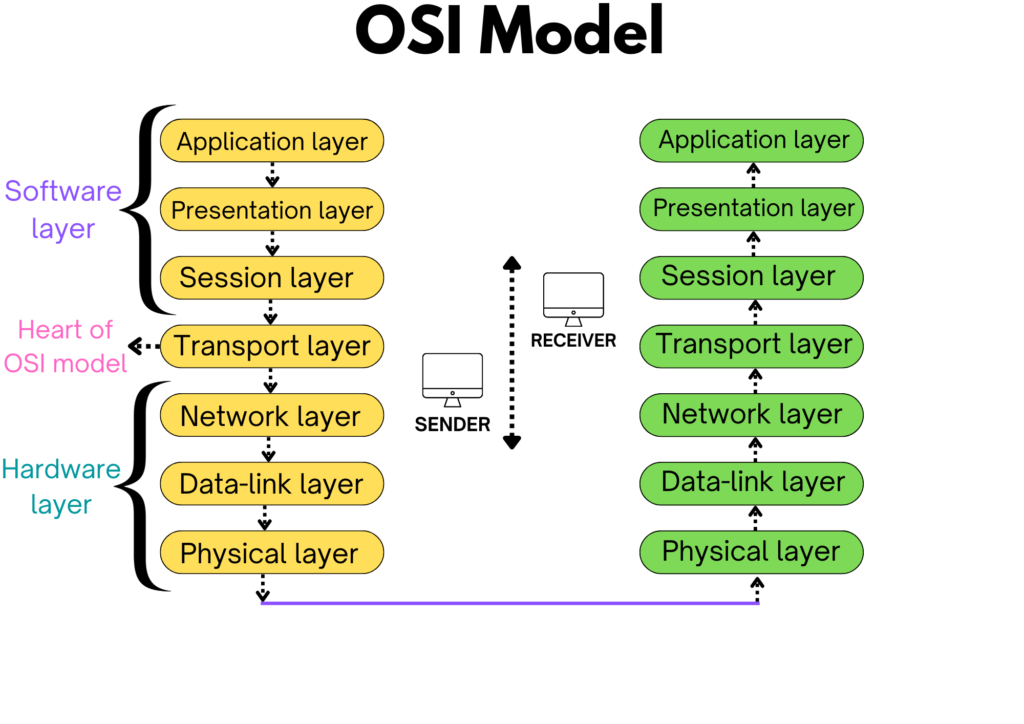
OSI model stands for open system interconnection model it has 7 layer architecture where each layer has its functionality and all 7 layers work collaboratively to transmit the data from one network to another across the globe.
It was developed by International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Layers of OSI model
There are seven layers of the OSI model and they are as follows
- Application layer
- Presentation layer
- session layer
- Transport layer
- Network layer
- data link layer
- physical layer
all 7 layers work collaboratively to transmit the data from one network to another across the globe. understand the working of the OSI model from the below figure.
Application layer
- Application layer is the top most layer of the OSI model.
- It is a layer through which users can interact.
- It provides services to the users.
- Application layer programs are based on the client-server model.

Function of Application layer
- Identify a communication partner to transmit data (basically, it identifies where to send data through an IP address).
- Determine resource availability (Basically, it checks whether sufficient network resources are available for required communication or not)
- Synchronizing communication.
Services provided by Application layer
- File transfer
- Accessing a file
- managing a file
- Addressing (Identify where to send data through IP address).
- Mail services (Example email)
- Directory services
Presentation layer
- Presentation layer is also called a translation layer.
- It converts one form of code into another form (Encryption & decryption).
- It is concerned with the syntax & semantics of data or information.
- Data compression,data encryption & decription done in presentation layer.
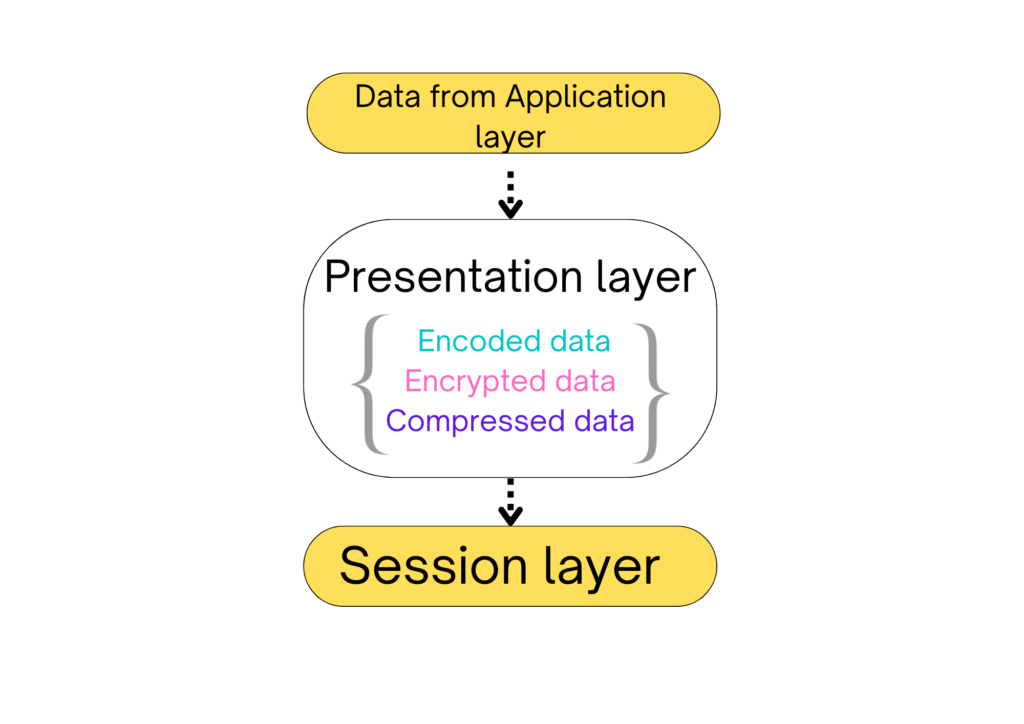
Function of the Presentation layer
- Translation (ASCII to EBCDIC).
- It can do Encryption & Decryption.
- Compression (It reduces the number of bits to transmit on a network).
Session layer
Session layer allowed and handled the establishment of a connection between two processors, it can use that connection, maintain that connection and terminate that connection whenever it is required.

Function of the Session layer
- Session establishment,maintenance & termination of connection.
- Synchronization of data.
- Dialog controller (It decided which device will communicate first and the amount of data that will be sent).
Transport Layer
The transport layer is the heart of an OSI model and it is operated by the operating system.
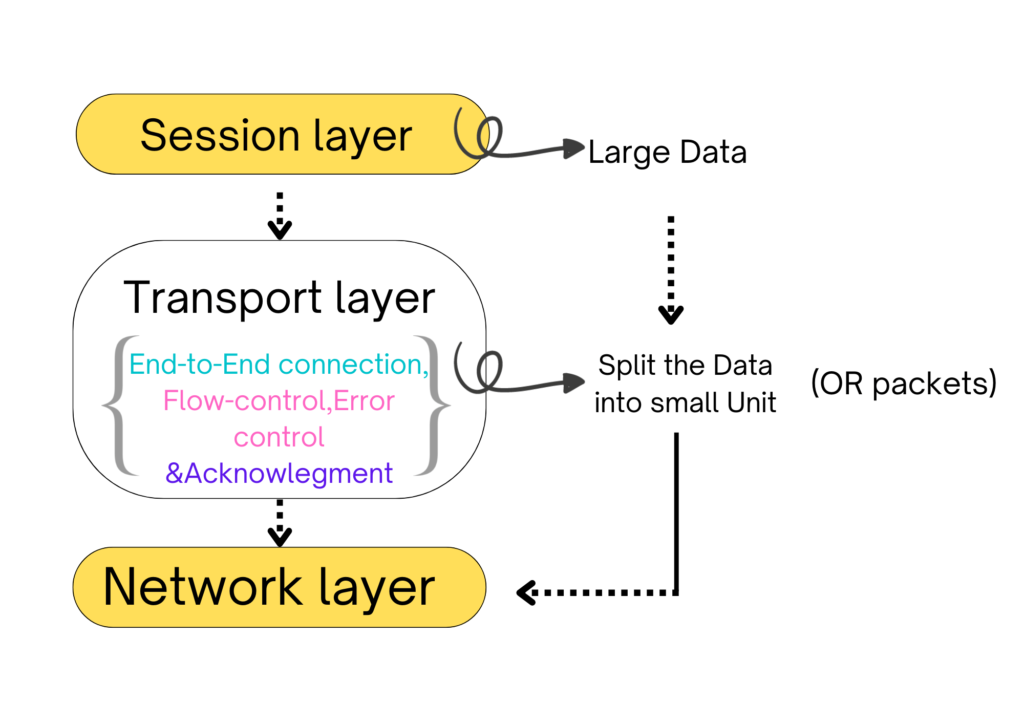
Function of Transport layer
- It decides if data transmission should be parallel & Single path.
- Multiplexing and splitting of data are done by this layer.
- Converting messages to a smaller unit.
- Responsible for End to End Delivery of the complete message.
- It gives Aknowlegment, whether data is sent or not.
Services provided by Transport layer
there are mainly two services provided by the Transport layer.
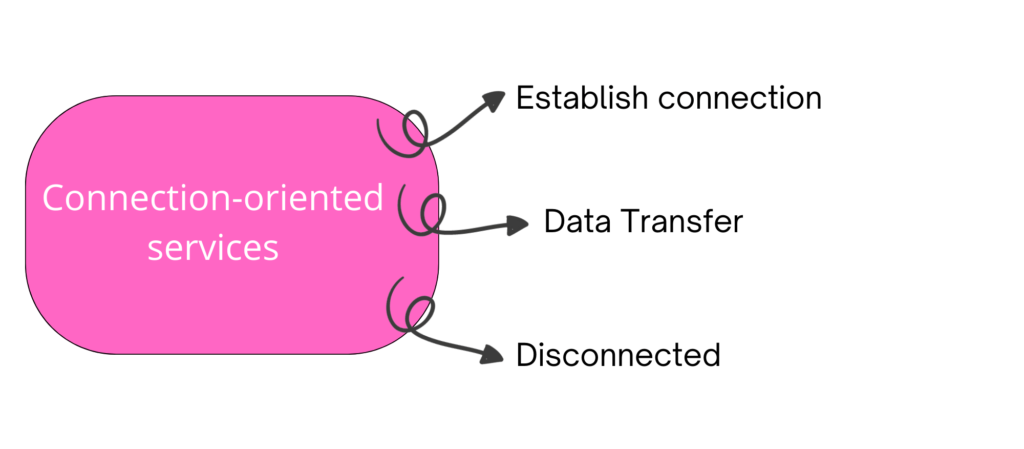
- Connection-Oriented services
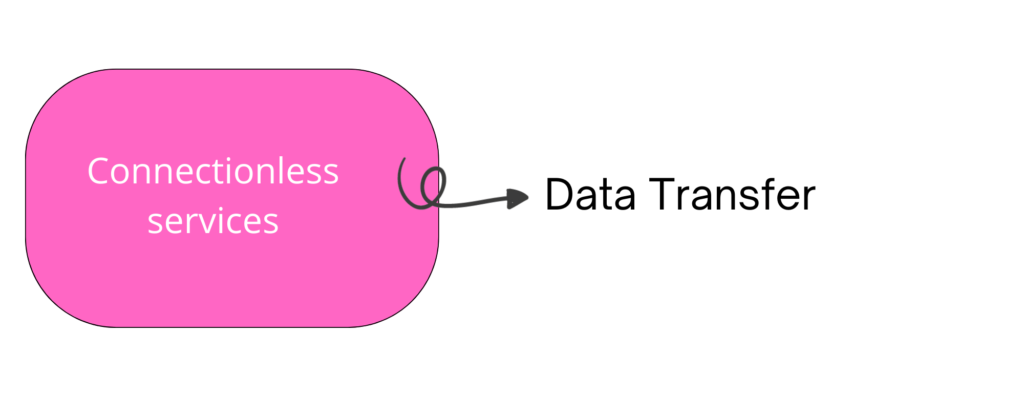
- Connectionless services
There are three phases of connection-oriented services in the Transport layer as shown below figure.
There is only one phase of connectionless services in the Transport layer as shown below.
Network layer
- Controls the operation of the subnet.
- Routing packets from source to destination. It selects the shortest path to transmit packets from a number of the router available.
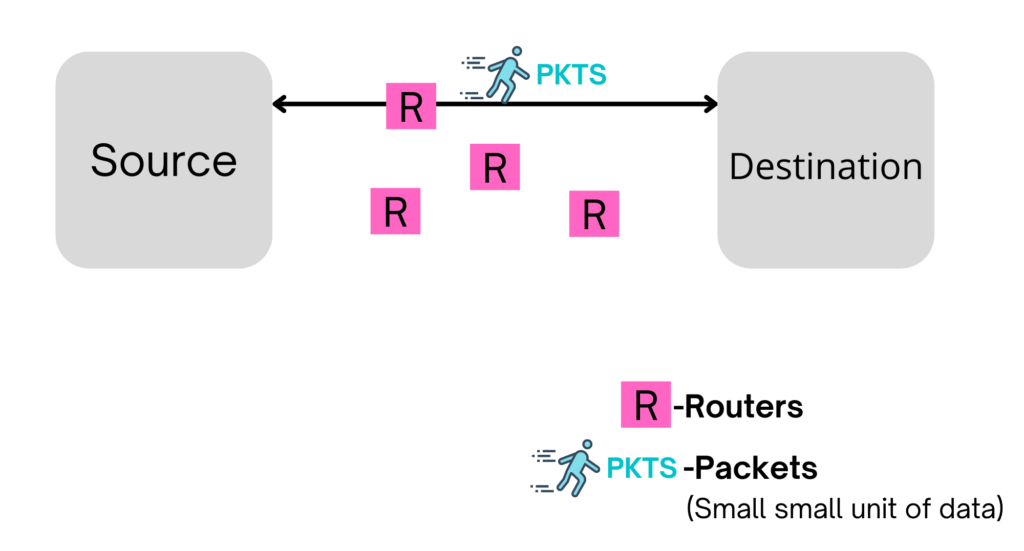
- IP address header has to place in the Network layer.
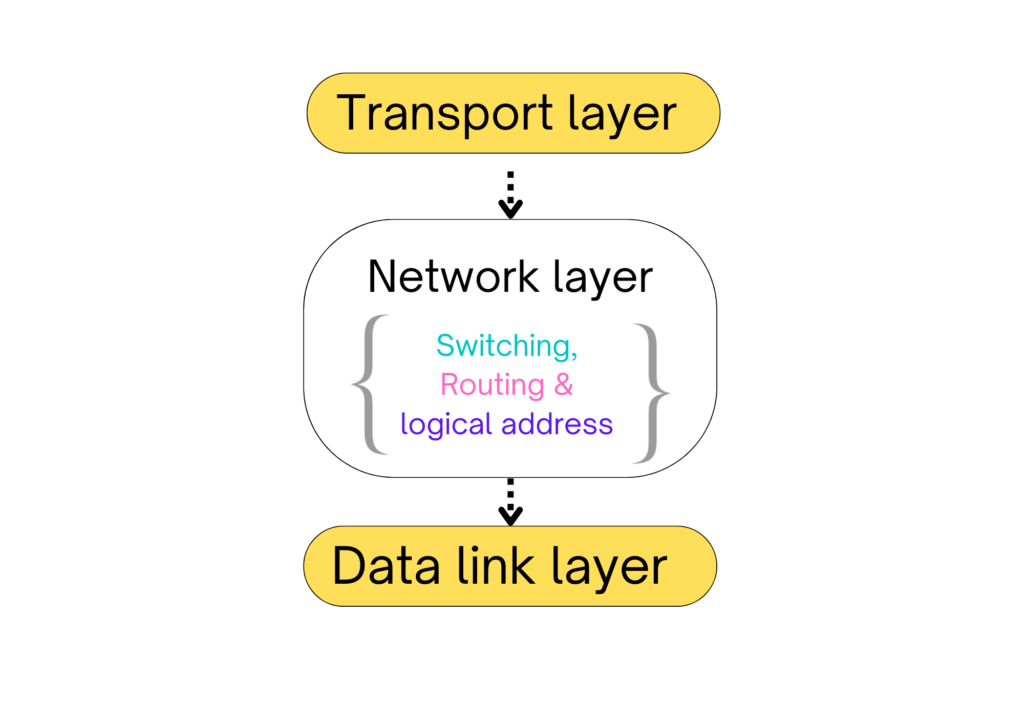
Functions of Network layer
- Routing (Select which route is suitable to transfer data from source to destination)
- Logical address (to transmit packets you have to know the logical address of the router).
data link layer
- It is responsible for a node to node (source to destination) delivery of messages.
- Error control. (check whether the data is correct or not )
- packets received from the network layer are further divided into frames depending on the frame size of the network interface card (NIC).
- When the frame buffer is full, it stops the transmitting signal.
- switch & bridge are used as data-link layer devices.
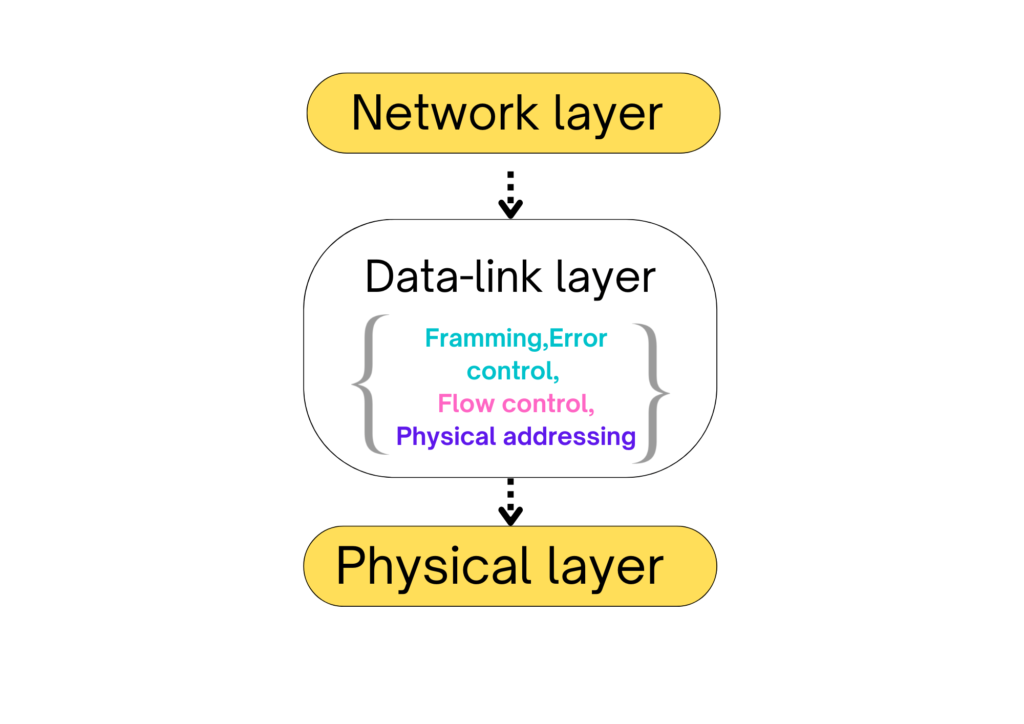
Function of Data Link Layer
- Framing (packets are divided into frames in the data link layer)
- Physical Addressing (Data link layer adds a physical address of sender/receiver in the header of each frame).
- Error control.
- Flow control (It controls the amount of data to be sent)
- Access control.
Physical Layer
- It is the lowest layer of the OSI model.
- It activates, maintains & deactivates the Physical connection.
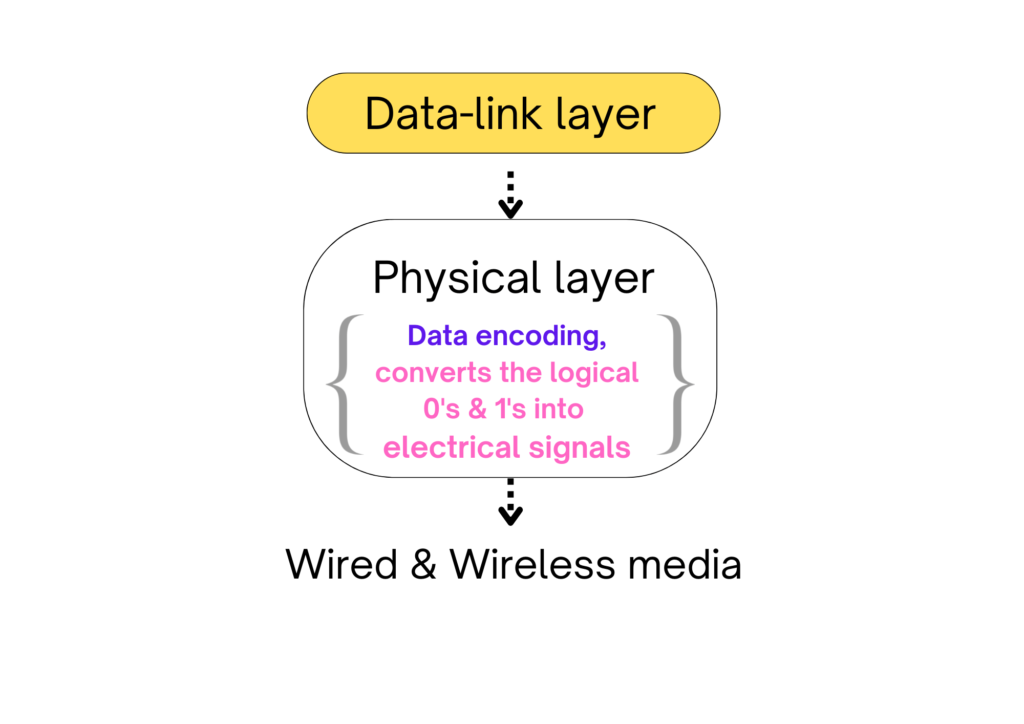
- It converts the logical 0’s & 1’s into electrical signals.
- Data encoding is also done in this layer.
- Hubs, repeaters, modems, cables, etc are Physical devices.
Function of Physical layer
- Bit synchronization.
- Bit rate control.
- Physical topologies (Physical layer can be arranging different devices/nodes in-network with the help of bus topology, star topology, and mesh topology).
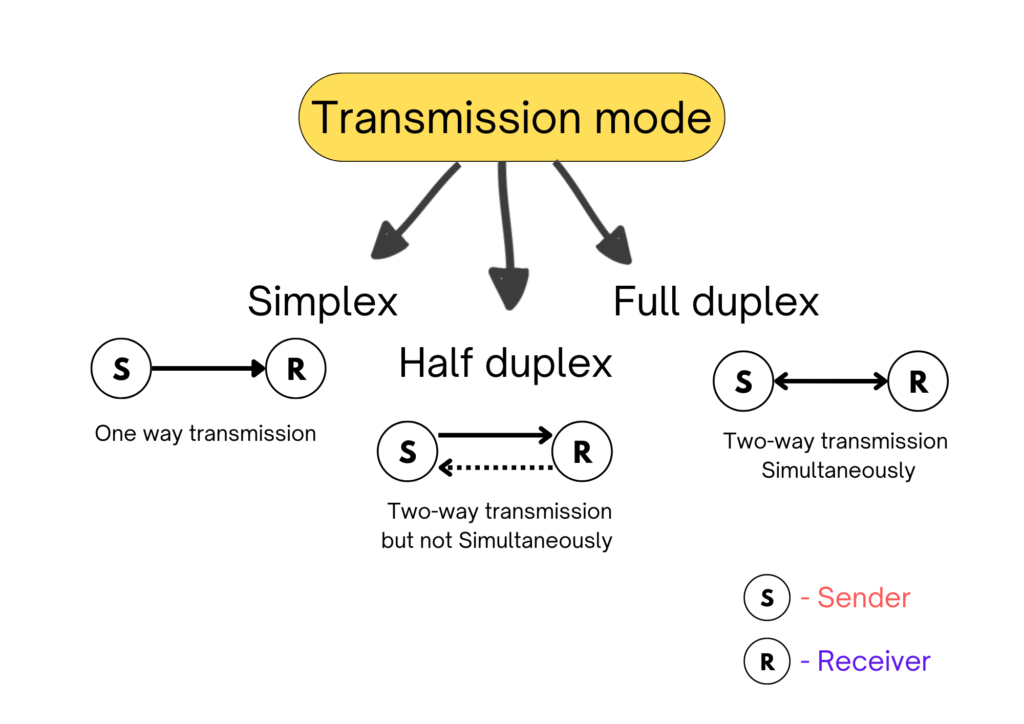
- Transmission mode (There are three modes to transmit data as shown below)
Hope this post adds some value to your life – thank you.