There are many special arrays in Numpy that you create using numpy built-in functions. So in this post, we will explore each of those functions to create a special numpy array with detailed explanations and examples.
You can also check out our previous article 👉 Introduction to NumPy in Python with Simple Example.
Array Filled with Zeros
There is a function called zeros() that is used to create an array filled with 0’s.
To create an array filled with 0’s, you need to specify the shape of your array as an argument inside the zeros() function.
Syntax: np.zeros(shape)
Create a 1D array filled with zeros:
import numpy as np
ar_zero = np.zeros(4)
print(ar_zero)Output:
[0. 0. 0. 0.]Create a 2D array filled with zeros:
import numpy as np
ar_zero2 = np.zeros((3,4))
print(ar_zero2)Output:
[[0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 0. 0.]]NOTE: Numpy arrays look and act very similarly to matrices. That’s why when we pass (3,4) as an argument inside the zeros() function, it creates an array with 3 rows and 4 columns. So, remember matrices whenever you specify the shape to create a numpy array.
Array filled with ones
There is a function called ones() that is used to create an array filled with 1’s. Inside the ones() function, you need to specify the shape of the array.
Syntax: np.ones(shape)
Create a 1D array filled with ones:
import numpy as np
ar_ones = np.ones(5)
print(ar_ones)Output:
[1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]Create a 2D array filled with ones:
import numpy as np
ar_ones2 = np.ones((3,5))
print(ar_ones2)Output:
[[1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]]Create an Empty array
There is a function called empty() that is used to create an empty array. Inside the empty() function, you need to specify the shape (how many sizes of empty array you want).
Syntax: np.empty(shape)
import numpy as np
ar_emp = np.empty(3)
print(ar_emp)Output:
[6.08532801e+247 4.44387685e+252 3.17095867e+180] It might be possible to see some data inside your empty array. This is because it shows previous data (or garbage data) that is present in your memory.
An Array with a range of elements
The arange() function is used to create an array with a specified range of elements.
Syntax: np.arange(start,end,step)
import numpy as np
ar_range = np.arange(1,6)
print(ar_range)Output:
[1 2 3 4 5]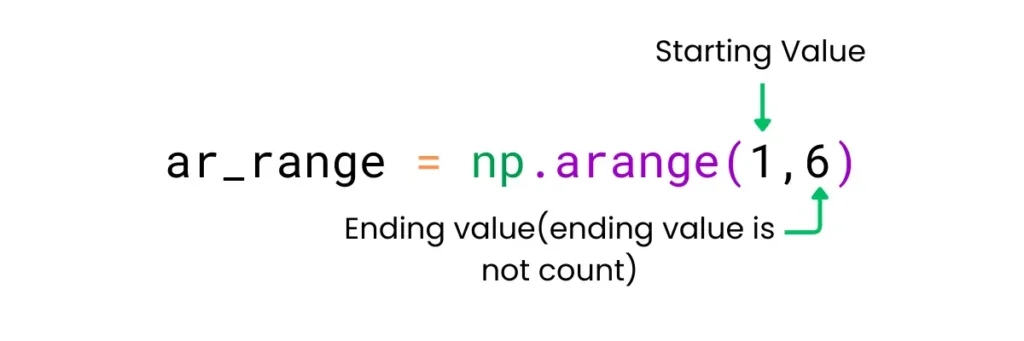
The arange() function works very similarly to the range() function of Python.
Array Diagonal element filled with 1’s (Identity Matrix)
The eye() function is used to create an array with diagonal elements filled with 1’s. Inside the eye() function, you need to specify the shape of the array. For example, if you pass 3, it will create a 3×3 array.
import numpy as np
i_matrix = np.eye(3)
print(i_matrix)Output:
[[1. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0.]
[0. 0. 1.]]Array with Values that are Spaced Linearly in a specified interval.
The linspace() function is used to create an array with values that are spaced linearly in a specified interval.
Inside the linspace() function you need to pass three arguments; starting range, ending range, and number of elements.
import numpy as np
l_space = np.linspace(1,10,num=5)
print(l_space)Output:
[ 1. 3.25 5.5 7.75 10. ]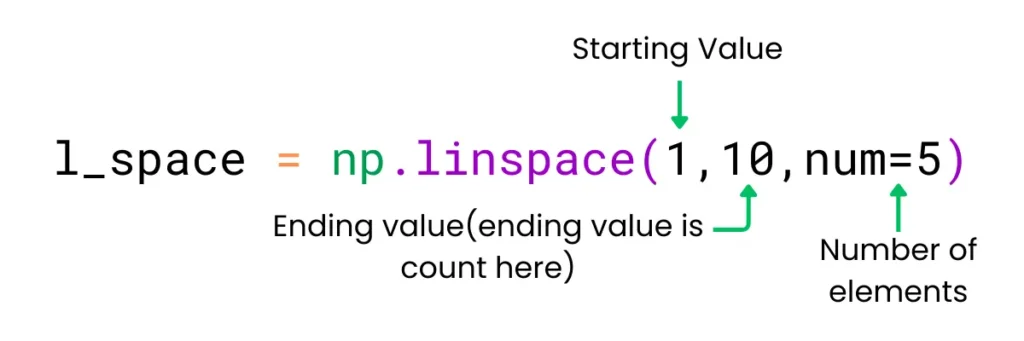
In simple terms, the linspace() function generates numbers within a specified range, ensuring that the difference between each consecutive pair of numbers remains the same.
This is all about special numpy arrays. I hope this post added some value to your life – Thank you.






