In this post, we will learn about numpy.random module, where we see how we can create a numpy array with random values with detailed explanations and examples.
You can also check out our previous article 👉 Special NumPy Array with Example
There are many built-in functions in the numpy.random module that are used to create a Numpy array with random values. Let’s discuss each of those functions one by one.
np.random.rand()
The rand() function is used to generate an array with random values between 0 to 1.
Syntax: np.random.rand(shape)
Create 1D array with rand() function:
import numpy as np
arr_rand = np.random.rand(5)
print(arr_rand)Output:
[0.02783847 0.87328351 0.22921382 0.5657408 0.17159723]Create 2D array with rand() function:
import numpy as np
arr_rand = np.random.rand(3,2)
print(arr_rand)Output:
[[0.07083235 0.78259026]
[0.37289517 0.60604745]
[0.27461912 0.61344845]]np.random.randn()
The randn() function is used to create an array with random values close to zero. This function may return positive or negative number as well.
Syntax: np.random.randn(shape)
Create 1D array with randn() function:
import numpy as np
arr_randn = np.random.randn(4)
print(arr_randn)Output:
[-0.94495002 0.97093534 0.12558914 -1.27040048]Create 2D array with randn() function:
import numpy as np
arr_randn = np.random.randn(2,2)
print(arr_randn)Output:
[[-0.11735794 -0.0397358 ]
[ 0.66068179 -2.14899386]]np.random.ranf()
The ranf() function is used for doing random sampling in NumPy. It returns an array of specified shape and fills it with random float numbers in the half-open interval [0.0, 1.0) (this means, In the ranf() function 0 is included and 1 is not).
Syntax: np.random.ranf(shape)
Create 1D array with ranf() function:
import numpy as np
arr_ranf = np.random.ranf(3)
print(arr_ranf)Output:
[0.01584818 0.76881585 0.21057889]Create 2D array with ranf() function:
import numpy as np
arr_ranf = np.random.ranf((3,3))
print(arr_ranf)Output:
[[0.37541137 0.94580039 0.97637302]
[0.92294981 0.92401746 0.12589338]
[0.8689295 0.40522533 0.69479186]]np.random.randint()
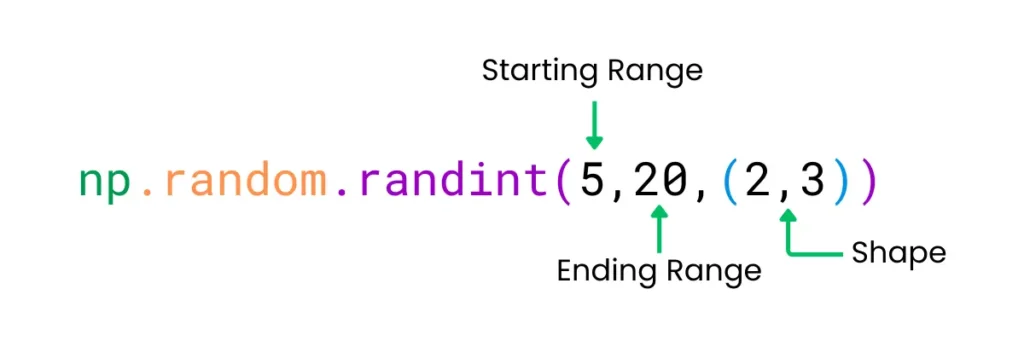
The randint() function is used to create an array with random values between given range.
Syntax: np.random.randint(start,end,shape)
import numpy as np
arr_randint = np.random.randint(5,20,(2,3))
print(arr_randint)Output:
[[13 9 17]
[18 15 5]]