In this post, we will learn about different data types in numpy and also we will see how we can convert data types of numpy array with detailed explanations and examples.
You can also check out our previous article 👉 Create a NumPy Array with Random Values
So, let’s start learning. First, we will explore all the data types of NumPy, and after that, we will try them with examples.
Data Types in NumPy
| Data Types | Description |
| bool_ | Boolean (True or False) stored as a byte. |
| int_ | Default integer type normally either int64 or int32 |
| intc | Identical to C int (normally either int32 or int64) |
| intp | Integer used for indexing (normally either int32 or int64) |
| int8 | 8-bit integer (-128 to 127) |
| int16 | 16-bit integer (-32,768 to 32,767) |
| int32 | 32-bit integer (-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647) |
| int64 | 64-bit integer (-9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807) |
| uint8 | 8-bit unsigned integer (0 to 255) |
| uint16 | 16-bit unsigned integer (0 to 65,535) |
| uint32 | 32-bit unsigned integer (0 to 4,294,967,295) |
| uint64 | 64-bit unsigned integer (0 to 18,446,744,073,709,551,615) |
| float_ | Short-hand for float64 |
| float16 | 16-bit floating-point number; Half precision floating-point; Sign (1 bit), Exponent (5 bits), Mantissa (10 bits) |
| float32 | 32-bit floating-point number; Single precision floating-point; Sign (1 bit), Exponent (8 bits), Mantissa (23 bits) |
| float64 | 64-bit floating-point number; Double precision floating-point; Sign (1 bit), Exponent (11 bits), Mantissa (52 bits) |
| complex_ | Short-hand for complex128 |
| complex64 | Complex number represented by two 32-bit floats (Real and imaginary component) |
| complex128 | Complex number represented by two 64-bit floats (Real and imaginary component) |
| string_ | Fixed-size ASCII strings |
| timedelta64 | timedelta type for representing time intervals |
| datetime64 | Date and time with nanosecond precision. |
| void | Void type used for structured arrays. |
Numpy also provides a feature to represent all the data types using their special characters. So let’s explore all the special characters used to represent data types in NumPy.
List of Characters that are Used to Represent Data Types in NumPy
i– integerb– booleanu– unsigned integerf– floatc– complex floatm– timedeltaM– datatimeO– objectS– StringU– Unicode StringV– void (fixed chunk of memory for other types)
Check data types of NumPy Array
To check the data type of a numpy array, you can use the dtype attribute.
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
print(arr.dtype)Output:
int32Create a NumPy Array with Specified Data Types
To create a NumPy array with a specified data type, you need to pass the dtype attribute as an argument inside the array() function.
import numpy as np
arr2 = np.array([1,2,3,4,5], dtype="int8")
print(arr2)
print(arr2.dtype)Output:
[1 2 3 4]
int8In NumPy, each data type has a corresponding built-in function, such as numpy.int8() for int8. You can also use these built-in functions in the dtype attribute to create arrays with specified data types.
import numpy as np
arr3 = np.array([2,4,6,8,10], dtype=np.int8)
print(arr3)
print(arr3.dtype)Output:
[ 2 4 6 8 10]
int8There is one more way to specify the dtype, which is to use special characters for data types.
import numpy as np
arr4 = np.array([1,2,3,4,5,6,7], dtype="f")
print(arr4)
print(arr4.dtype)Output:
[1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.]
float32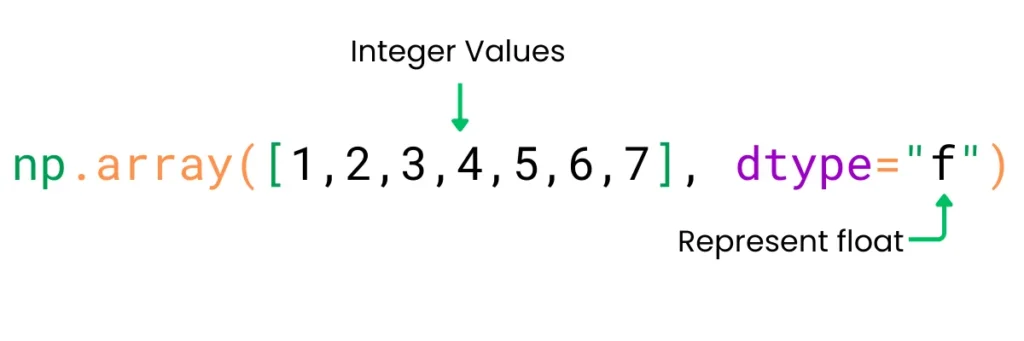
Convert Data Types of a Numpy Array
There is two ways to convert data types of an array:
- Using built-in functions &
- Using
astype()method
Using Built-in Function
As we have already discussed, each data type in NumPy has a corresponding function. We can use these functions to convert one data type into another.
Int → Float
import numpy as np
a1_int = np.array([1,2,3,5,7,11,13,17])
print(a1_int.dtype) # Output: int32
print(a1_int)
print()
# Convert int --> float
a1_float = np.float16(a1_int)
print(a1_float.dtype) # Output: float16
print(a1_float)Output:
int32
[ 1 2 3 5 7 11 13 17]
float16
[ 1. 2. 3. 5. 7. 11. 13. 17.]Float → Int
import numpy as np
a2_float = np.array([1,2,3,5,7,11,13,17], dtype="float32")
print(a2_float.dtype) # Output: float64
print(a2_float)
print()
# Convert float --> int
a2_int = np.int16(a2_float)
print(a2_int.dtype)
print(a2_int)Output:
float32
[ 1. 2. 3. 5. 7. 11. 13. 17.]
int16
[ 1 2 3 5 7 11 13 17]Using astype() method
The astype() function used to convert data types of an array. It takes the target data type as an argument, and it returns a new array with the same data but in the specified data type.
arr = np.array([1,2,3,4,5])
new_arr = arr.astype("float32")
print(new_arr.dtype) # Output: float32
print(new_arr)Output:
float32
[1. 2. 3. 4. 5.]





